Pre-job briefing – Communication Towers
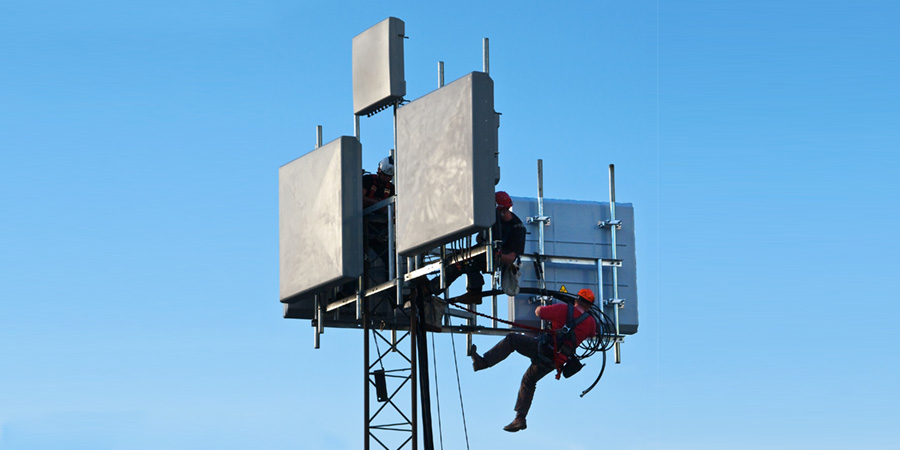

Over the past 30 years, the growing demand for wireless and broadcast communications has urged a dramatic increase in communication tower construction and maintenance.
In order to erect or maintain communication towers, employees regularly climb the towers, using fixed ladders, support structures or step bolts, varies from 30 to 100 meters height. They climb the towers throughout the year even in the time of adverse weather conditions.
Due to increased number of communication towers and the greater utility of existing towers, the number of injuries and fatalities associated with them have been on the rise. From 2013 to 2016, OSHA documented 34 fatalities at communication towers. OSHA is working with industry stakeholders to identify the causes of these injuries and fatalities, and to reduce the risks faced by employees in the communication tower industry.
Some of the more frequently encountered hazards include:
- Falls from heights
- Electrical hazards
- Hazards associated with hoisting personnel and equipment with base-mounted drum hoists
- Adverse weather conditions
- Equipment failure
- Structural collapse of towers
- Radio frequency Exposure
- Biological Hazard
The severities of hazards may be varying according to the different types of communication towers which are based upon their structural action, their cross-section, the type of sections used and on the placement of tower. Some of the most common towers used are monopole, lattice towers, guyed towers.
For E.g. The Monopole Tower is a single tube tower. It typically stands between 30-60 meters with antennas mounted on the exterior of the tower. It is designed for cables to run on the interior of the tower. When climbing monopoles, employee will find that their upper body gets fatigued faster than when climbing freestanding towers due to the greater vertical climb.
Keeping tower climbers safe should be a major part of climber training and a regular part of job and work reviews. Here are some pre-job briefing points are mentioned to keep in mind.
Tower Climbers and Ground Crew Workers
- All work crews must be provided with proper safety equipment & ensure its use.
- All climbing work should include comprehensive safety planning, including Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) and Emergency Action Plan (EAP), for every job site.
- All work crews should not be allowed to work at heights during adverse weather conditions like heavy rain, storm, heat, etc.
- All work crews should continually seek to enhance their safety skills and awareness through regular trainings and awareness programs.
- Particular attention should be paid to inspections, including equipment inspections and PPE inspections.
- It must be ensured that there is always a competent person on site and should monitor the mental and physical wellbeing of climbers.
- The supervisors should conduct pep talk/ tool box talk at the beginning of each work day. In which the possible hazards and its control measures specific to the jobsite, emergency preparedness, etc. should be highlighted.
- Tower climbers and ground crew employees should know how to report unsafe conditions and should follow applicable reporting processes whenever they are discovered.
Some of the basic techniques to be adopted during climbing the towers
- Assess the situation.
- Look for hazards and try to find the least obstructed route to the area.
- Some hazards to look for are power lines, flying insects, missing members, excessive corrosion and adverse weather conditions.
- Climber should inspect his gear and suit up (Harness, lanyards, rope grab and bolt bags)
- Maintain a three‐point stance at all times and make sure you have a good grasp and use your upper body to maintain balance but avoid over‐squeezing with your hands.
- Whenever climbing vertical, try to use your legs as much as possible.
- When climbing on diagonals, position your body weight to the outside of the slope or outside of your foot. Avoid placing your body weight directly over your foot to prevent slippage.
- Continually look for loose or missing members, missing bolts, or any other hazards you may have missed from the ground.
Protection from radiation exposure
- Employees shall not enter areas where Radio Frequency Radiation (RFR) exposure levels are above the criteria.
- The employer shall institute measures to ensure that the employee’s exposure is not greater than that permitted by the radiation guide. Such measures shall include, but not be limited to, those of an administrative or engineering control or involving personal protective equipment.
- Employers can have monitoring devices on their site while work is being performed.
Remote communication sites
- Employees should aware about the facilities available at remote communication tower site such as vehicle, communication devices, emergency survival equipment not limited to:
- Reliable water and food.
- Reliable communication plan.
- Depends upon the number of employees, and the hazards anticipated at the worksite, number of first aid kits to be made available.
Training
- Contractors should ensure that all employees whoever involved in climbing the communication towers are trained for their tasks which is to be performed.
- Contractors should ensure that new employees should be taken care and undergo comprehensive training as authorized climbers. They can be paired with an experienced climber as an apprentice until they have enough experience and climbing hours to undertake the competent climber training.
- Employees who will be expected to perform rigging or hoisting activities should have specialized training to ensure they can safely perform these tasks.